Aero-acoustics noise generated from building parts
HOME <Aeroacoustics Solutions < <Aeroacoustic Noise generated from buildings < Aero-acoustics noise generated from building partsIn general, these external parts are surrounding the building or located on the roof of the building. These parts ( veils or curtains, balustrades, sunshades, grids…) are made of elements that are equally spaced from each other. Depending on the wind speed and directions, the interaction of a vortex shed from an element with the next element can generate an aerodynamic noise characterized by one or multi tones. Also, the passage of the wind through an open and confined space such as a cavity or grid geometry can generate a tonal noise (cavity or Helmholtz noise).
The Beetham tower in Manchester (UK) is a well known case where a glass plate placed on the roof of the tower generates a tonal noise characterized by very high and annoying peak for high wind speeds.
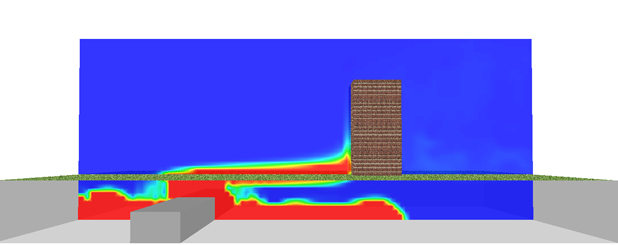
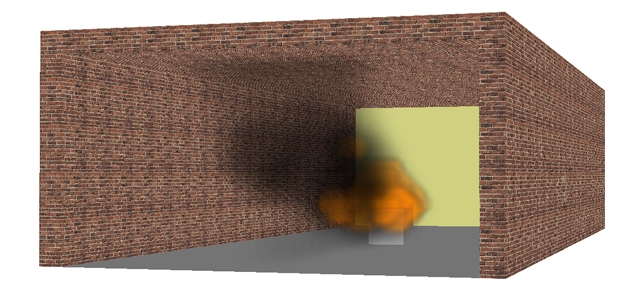
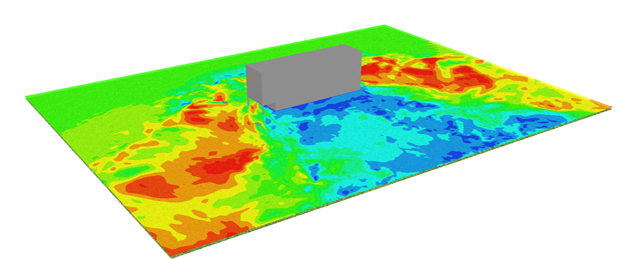
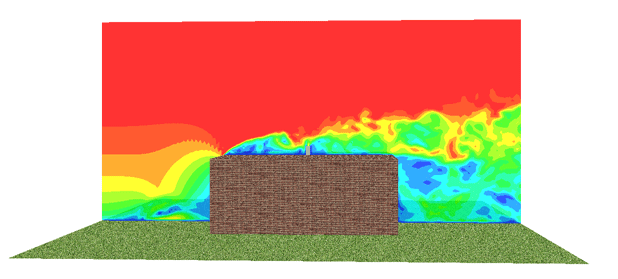
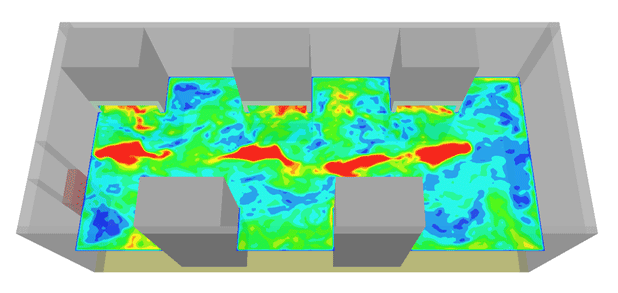
In the figures below, results from a CFD modeling of a simplified model of a curtains made of grid elements are shown. The objective of the modeling was to investigate the noise generated from the plate when the wind passes over the grid elements.
 |
|
| Instantaneous velocity distribution around the blade | |
 |
 |
| Sample of pressure fluctuations recorded at one sensor | Pressure fluctuations in the frequency domain |
The recorded transient pressure fluctuations (left figure) were analysed in the frequency domain to show if there are emerging peaks associated with these fluctuations. This was achieved by using a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). As shown in the right figure, a dominant peak or tone is occurring around a Strouhal number of 0.3 (for a cylinder the characteristic Strouhal number is 0.2). A second peak (or harmonic) occurs around 0.54. The dominant frequency can be compared to the resonant or natural frequency or frequencies of the curtain grid to determine if an aero-acoustic resonance is occurring which is not desirable as this phenomenon is characterized by a high whistling noise.
Related Animation: Instantaneous pressure distribution around the blade