Building Thermal modeling
HOME <Building Solutions < Building Thermal modelingEASTechnology provides building thermal modeling and testing services to design and mechanical teams and building owners. We use Infrared Thermography and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) models to evaluate a wide variety of building thermal problems.
Our Building Thermal Modeling (BTM) Solutions services include:
Thermal Imaging Analysis
Efficient building insulation improves occupant comfort, reduces energy consumption, increases equipment performance and longevity, and reduces building maintenance and operating costs. Infrared Thermography based on Thermal Imaging method uses a thermal camera to record the instantaneous surface wall temperature distribution for an existing building. Depending on the wall dimensions, several zones of the wall can be analyzed. Using Infrared Thermography, we can measure the following:
- Building wall assessments
- Instantaneous wall surface temperatures
- Temperature profiles at a given location
- Temperature histograms
- Temperature statistics
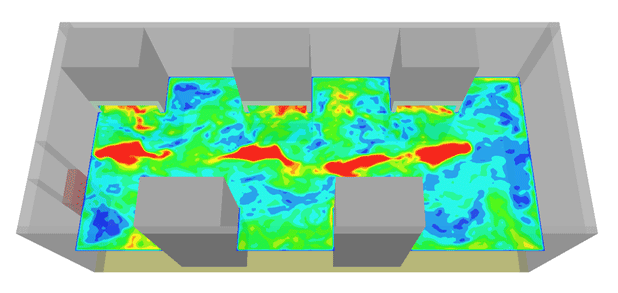
In the below images, we used a thermal camera to analysis the temperature distribution at the surface of a wall made of iron.
- The right image corresponds to a zone located at the middle of the wall.
- The middle image represents the temperature profile along a horizontal line with the highest temperature value occurring at almost the middle of the structure.
- The left image shows the temperature histogram along the horizontal line.
 |
 |
 |
| Thermal Imaging: Surface Temperature | Thermal Imaging: Surface Temperature | Temperature histogram along the horizontal line |
CFD Thermal modeling
In addition to Thermal Imaging methods, our CFD capabilities can be used to assess how good the wall insulation is. We can assess the following:
Steady state and transient temperature distributions
- Effect of the material properties
- Effect of wall thickness
- Heat dissipation
- Building wall assessments
- Design optimization
In the assessment, the thermal properties of the material can be constant or function of the temperature. Different boundary conditions can be applied such as temperature, heat flux and adiabatic walls (perfect insulation).
In the below figures, we used CFD modeling to assess the thermal behavior of a wall made of one and two materials. In both modeling, one side of the wall was exposed to a constant temperature of 20o C (room temperature) and -5o C (winter conditions) on the opposite side of the wall.
 |
 |
 |
|
Temperature distribution along a wall made of a concrete material – Steady state solution |
Temperature distribution along a wall made of steel and concrete materials – Steady state solution |
The last 2 bottom charts correspond to results from transient simulations for the wall made of one material.
The transient temperature is predicted at a sensor located at the middle of the wall. After 1500 [s], the solution converges towards a steady solution with a value of about 11.2 o C.
The total losses for this example are predicted to be around 0.25 KW once the simulation has reached a steady state solution. All these losses are due to the heat by conduction through the wall.
 |
 |
| Temperature distribution in the middle of the wall – Transient solution |
Heat losses by conduction through the wall – Transient solution |